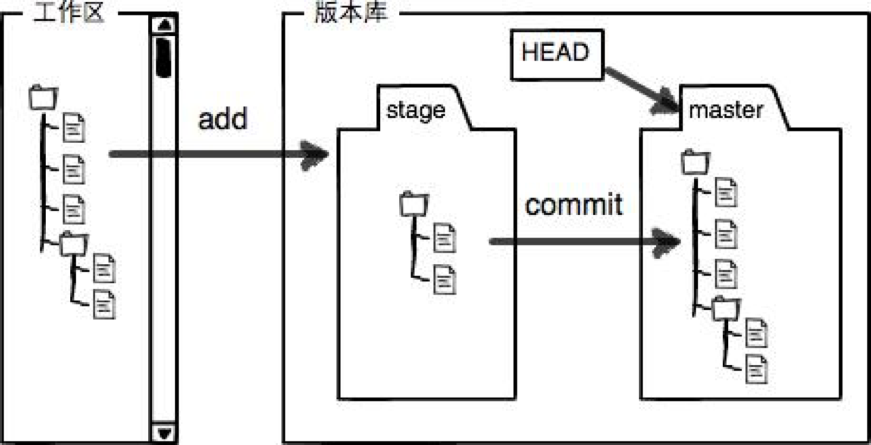
一些常用指令
Merge your branch after CR:
Before merge your branch to mainline, you first need to get the most recent mainline code:1
2
3
4
5git checkout mainline
git pull
git checkout <branch_name>
git merge mainline
git push
After that, you can merge your branch:
1 | git checkout mainline |
.gitignore
.gitignore 文件只能作用于 Untracked Files,也就是那些从来没有被 Git 记录过的文件(自添加以后,从未 add 及 commit 过的文件)。
规则不生效,是因为那些 .log 文件曾经被 Git 记录过,因此 .gitignore 对它们完全无效。
- 从 Git 的数据库中删除对于该文件的追踪;
- 把对应的规则写入 .gitignore,让忽略真正生效;
- 提交+推送。
- 取消track,保留git里的文件(保留本地文件):
git update-index --assume-unchanged -pathgit update-index --no-assume-unchanged -path可以取消忽略文件- 但是忽略的文件多了,想找出所有被忽略的文件:
git ls-files -v | grep '^h\ '
- 取消track,保留git里的文件(保留本地文件):
git update-index --skip-worktree –pathgit update-index --no-skip-worktree –path可以取消忽略文件- 但是忽略的文件多了,想找出所有被忽略的文件:
git ls-files -v | grep ^S
- 取消track, 删除git里的文件:
git rm --cached -path
回退到上一个版本,回退到某一特定的commit快照:
1 | git reset --hard HEAD^ |
Checkout
管理的是修改不是文件
git checkout -- readme.txt
命令git checkout – readme.txt意思就是,把readme.txt文件在工作区的修改全部撤销,这里有两种情况:
一种是readme.txt自修改后还没有被放到暂存区,现在,撤销修改就回到和版本库一模一样的状态;
一种是readme.txt已经添加到暂存区后,又作了修改,现在,撤销修改就回到添加到暂存区后的状态。
总之,就是让这个文件回到最近一次git commit或git add时的状态
Git同样告诉我们,用命令git reset HEAD file可以把暂存区的修改撤销掉(unstage),重新放回工作区
场景1:当你改乱了工作区某个文件的内容,想直接丢弃工作区的修改时,用命令git checkout – file。
场景2:当你不但改乱了工作区某个文件的内容,还添加到了暂存区时,想丢弃修改,分两步,第一步用命令git reset HEAD file,就回到了场景1,第二步按场景1操作。
场景3:已经提交了不合适的修改到版本库时,想要撤销本次提交,参考版本回退一节,不过前提是没有推送到远程库
删除
rm test.txt
- 确认要删,git commit
- 误删 git checkout – file
分支
- 查看分支:
git branch - 创建分支:
git branch <name> - 切换分支:
git checkout <name> - 创建+切换分支:
git checkout -b <name> - 合并某分支到当前分支:
git merge <name> - 删除分支:
git branch -d <name>
当Git无法自动合并分支时,就必须首先解决冲突。解决冲突后,再提交,合并完成。
用git log –graph命令可以看到分支合并图
- 命令git push origin
可以推送一个本地标签; - 命令git push origin –tags可以推送全部未推送过的本地标签;
- 命令git tag -d
可以删除一个本地标签; - 命令git push origin :refs/tags/
可以删除一个远程标签
Branch Track
1 | git branch -u origin/<branch name> |
Rebase: 合并commit
git rebase -i HEAD~3git rebase -i 3a4226b
如果git rebase 有冲突
1 | git add . |
如果想放弃rebase
git rebase --abort
强制push
git push origin master --force
git add -u: 将文件的修改、文件删除,添加到暂缓区git add .: 将文件的修改、文件的新建,添加到暂缓区git add -A: 两者的结合,修改,新建,删除
远程仓库
查看远程仓库信息
1 | # 查看关联的远程仓库的名称 |
添加远程仓库的关联
1 | # git_url 为你的远程仓库的 url,可采用 http 协议或 ssh(git) 协议 |
删除远程仓库的关联
git remote remove <name>
修改远程仓库的关联
git remote set-url <name origin/upstream> <newurl>
远程分支
创建
git push -u origin mybranch
删除
git push origin --delete <branchName>
Commit大文件无法push
git log查看提交历史git reset commit_id 撤销未被传送到远程代码库的提交
Pull Request
https://www.cnblogs.com/kidsitcn/p/5319282.html
Git fork出来的project和上游project同步更新
问题描述:当我们在github上fork出一个项目后,如果原有的项目更新了,怎样使我们fork出来的项目和原有项目保持同步呢?怎样提交我们的代码更新呢?即怎样保持fork出的项目和上游项目保持更新,怎样创建pull request?关键步骤是使用git 的rebase命令。
步骤:
- 在 Fork 的代码库中添加上游代码库的 remote 源,该操作只需操作一次即可。
如: git remote add upstream https://github.scm.corp.ebay.com/montage/frontend-ui-workspace
其中 #upstream 表示上游代码库名, 该名字可以任意。
- 将本地的修改提交commit
- 在每次 Pull Request 前做如下操作,即可实现和上游版本库的同步。
3.1 : git remote update upstream
3.2 : git rebase upstream/{branch name}
需要注意的是在操作3.2之前,一定要切换到到{branch name}所指定的branch,如切换到develop branch
执行: git checkout develop
当然还有更简单的方法,即执行git pull upstream {branch name}
- Push 代码到 Github
git push
- 然后可以去github上自己的托管空间上创建pull request。
Folk Repo 保持master始终和Upstream同步
Current GitHub Collaboration Flow
Recommended method via Ry’s Git Tutorial
“Never, ever rebase commits that have been pushed to a shared repository.”–Hodson, Ryan
1 | git checkout -b css-edits |
A shortcut to the git fetch origin then git rebase origin/master is to git pull --rebase.
Be sure to git branch -d before rebasing origin/master, otherwise when you delete your local branch later, you’ll run into an not fully merged error like this:
SSH
SSH key放在本地.ssh/文件下
Create and test the ssh key
Create a repo. Make sure there is at least one file in it (even just the README) Generate ssh key:
1 | ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "your_email@example.com" |
Copy the contents of the file ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub to your SSH keys in your GitHub account settings. Test SSH key:
1 | ssh -T git@github.com |
Modify .ssh/config file
1 | vim ~/.ssh/config |
Add code like this:
1 | Host * |
Git Commit Template
Download template file: https://gist.github.com/ChenX1993/38c99c3014aad0c134818b9beaa7a89b
And run:
1 | git config --global commit.template ~/.git-commit-template.txt |